Redox Mediator as Highly Efficient Charge Storage Electrode Additive for All‐Solid‐State Lithium Metal Batteries
Advanced Energy Materials, Volume 15, Issue 11, March 18, 2025.

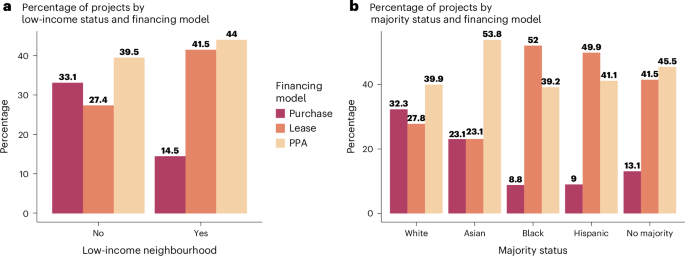
A simple cathode additive strategy is proposed to enhance the charge transfer and mass transport in ASSLBs by using CH6NI as a redox mediator additive in LiFePO4 cathode. The strategy effectively promotes the electron and ion transport in the cathode, facilitating the reaction kinetics during the delithiation/lithiation process of LiFePO4.
Abstract
All-solid-state lithium metal batteries (ASSLBs) have the potential to provide a significant increase in energy density and safety. However, most ASSLBs are still suffering from low cathode loading, poor rate capability, and low attainable energy/power densities, which seriously limit their practical application. Besides developing solid electrolytes with high conductivity, constructing a highly loaded cathode with rapid reaction kinetics is also essential for achieving high-performance ASSLBs. Herein, the methylamine hydroiodide (CH6NI) is investigated as a functional electrode additive to enable rapid Li+ transport and charge transfer in LiFePO4 (LFP) cathode, whereby the CH6NI serves as a charge storage carrier that facilitates the reaction kinetics during the delithiation and lithiation process of LFP. As a result, the ASSLB assembled with LFP@CH6NI cathode shows excellent cycling stability over 700 cycles at 2 C with a high capacity retention of 87.6%, while the cell with bare LFP cathode shows no capacity at high current rates (≥0.5 C). Moreover, the ASSLB pared with a high active loading cathode (5.6 mg cm−2) still exhibits a high specific capacity of 144.9 mAh g−1 at 0.5 C. This work provides a facile strategy that opens new possibilities for designing high-loading electrodes for high-performance ASSLBs.









































































































































































.jpg)

.jpg)





