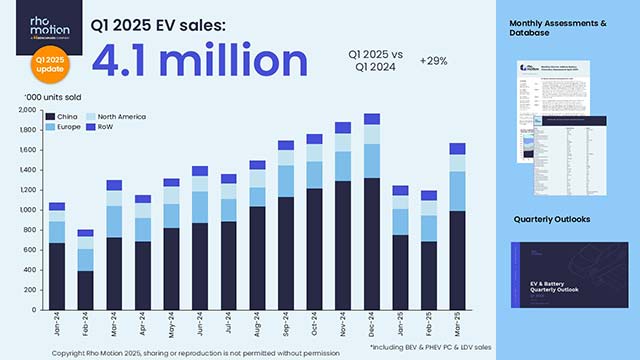
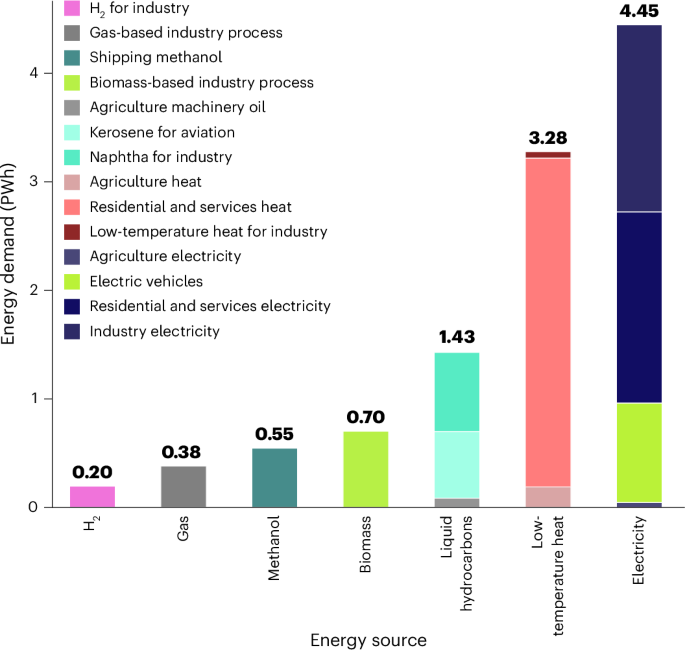
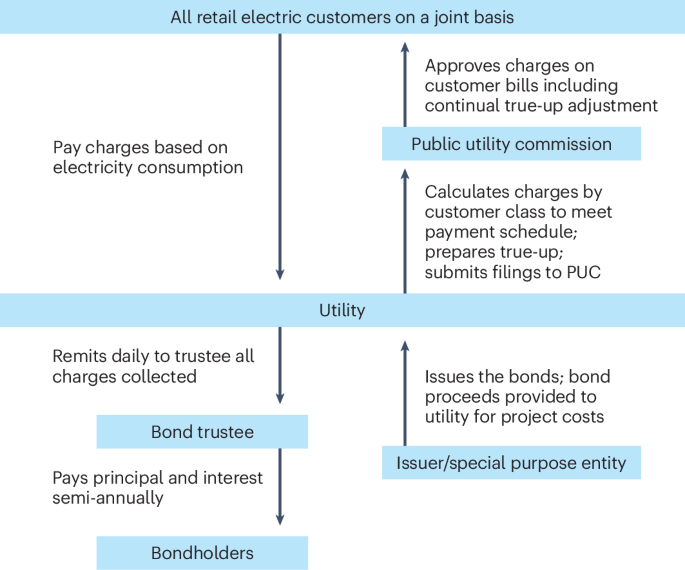
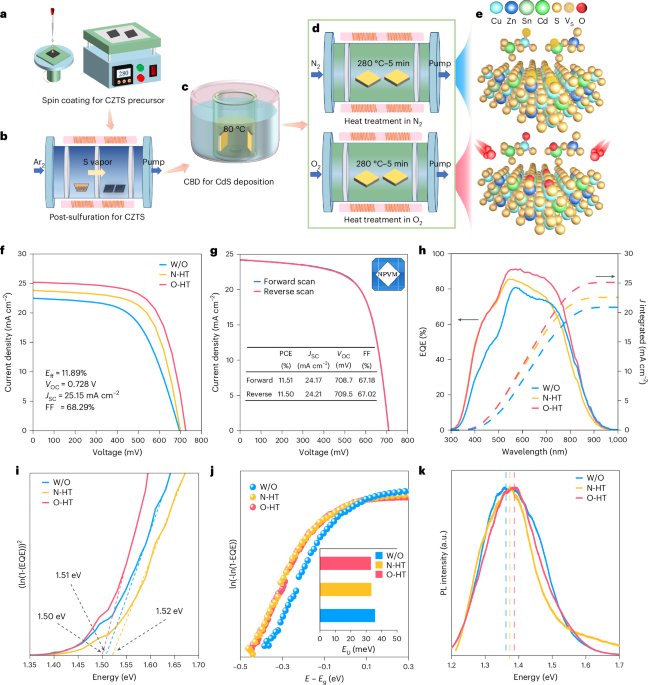
Mapping the ultrastructural topology of the corynebacterial cell surface
by Buse Isbilir, Anna Yeates, Vikram Alva, Tanmay A. M. Bharat Corynebacterium glutamicum is a diderm bacterium extensively used in the industrial-scale production of amino acids. Corynebacteria belong to the bacterial family Mycobacteriaceae, which is characterized by a highly unusual cell envelope with an outer membrane consisting of mycolic acids, called mycomembrane. The mycomembrane is further coated by a surface (S-)layer array in C. glutamicum, making this cell envelope highly distinctive. Despite the biotechnological significance of C. glutamicum and biomedical significance of mycomembrane-containing pathogens, ultrastructural and molecular details of its distinctive cell envelope remain poorly characterized. To address this, we investigated the cell envelope of C. glutamicum using electron cryotomography and cryomicroscopy of focused ion beam-milled single and dividing cells. Our cellular imaging allowed us to map the different components of the cell envelope onto the tomographic density. Our data reveal that C. glutamicum has a variable cell envelope, with the S-layer decorating the mycomembrane in a patchy manner. We further isolated and resolved the structure of the S-layer at 3.1 Å-resolution using single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Our structure shows that the S-layer of C. glutamicum is composed of a hexagonal array of the PS2 protein, which interacts directly with the mycomembrane via an anchoring segment containing a coiled-coil motif. Bioinformatic analyses revealed that the PS2 S-layer is sparsely yet exclusively present within the Corynebacterium genus and absent in other genera of the Mycobacteriaceae family, suggesting distinct evolutionary pathways in the development of their cell envelopes. Our structural and cellular data collectively provide a topography of the unusual C. glutamicum cell surface, features of which are shared by many pathogenic and microbiome-associated bacteria, as well as by several industrially significant bacterial species.
by Buse Isbilir, Anna Yeates, Vikram Alva, Tanmay A. M. Bharat Corynebacterium glutamicum is a diderm bacterium extensively used in the industrial-scale production of amino acids. Corynebacteria belong to the bacterial family Mycobacteriaceae, which is characterized by a highly unusual cell envelope with an outer membrane consisting of mycolic acids, called mycomembrane. The mycomembrane is further coated by a surface (S-)layer array in C. glutamicum, making this cell envelope highly distinctive. Despite the biotechnological significance of C. glutamicum and biomedical significance of mycomembrane-containing pathogens, ultrastructural and molecular details of its distinctive cell envelope remain poorly characterized. To address this, we investigated the cell envelope of C. glutamicum using electron cryotomography and cryomicroscopy of focused ion beam-milled single and dividing cells. Our cellular imaging allowed us to map the different components of the cell envelope onto the tomographic density. Our data reveal that C. glutamicum has a variable cell envelope, with the S-layer decorating the mycomembrane in a patchy manner. We further isolated and resolved the structure of the S-layer at 3.1 Å-resolution using single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Our structure shows that the S-layer of C. glutamicum is composed of a hexagonal array of the PS2 protein, which interacts directly with the mycomembrane via an anchoring segment containing a coiled-coil motif. Bioinformatic analyses revealed that the PS2 S-layer is sparsely yet exclusively present within the Corynebacterium genus and absent in other genera of the Mycobacteriaceae family, suggesting distinct evolutionary pathways in the development of their cell envelopes. Our structural and cellular data collectively provide a topography of the unusual C. glutamicum cell surface, features of which are shared by many pathogenic and microbiome-associated bacteria, as well as by several industrially significant bacterial species.