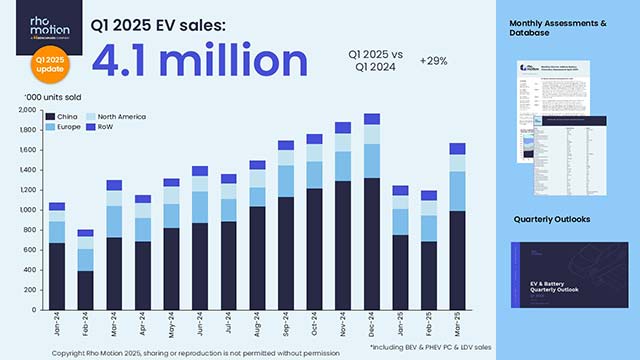
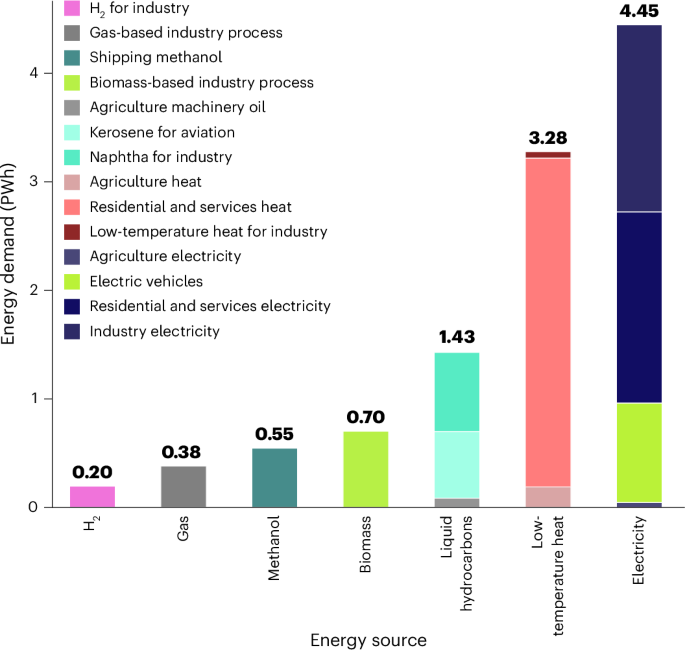
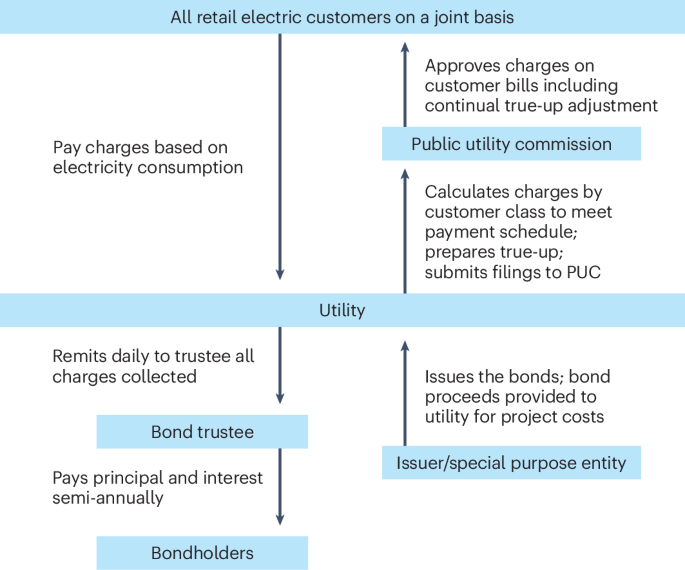
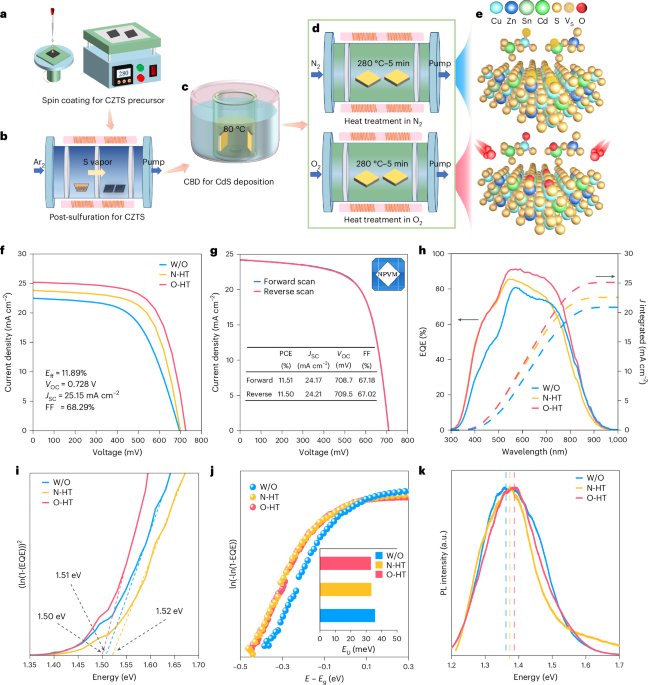
Concurrent electrode-electrolyte interfaces engineering via nano-Si3N4 additive for high-rate, high-voltage lithium metal batteries
Energy Environ. Sci., 2025, Accepted ManuscriptDOI: 10.1039/D4EE03862B, Paper Open Access   This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Jinuk Kim, Dong Gyu Lee, Ju Hyun Lee, Saehun Kim , Cheol-Young Park, Jiyoon Lee, Hyeokjin Kwon, Hannah Cho, Jungyoon Lee, Donghyeok Son, Hee-Tak Kim, Nam-Soon Choi, Tae Kyung Lee, Jinwoo LeeElectrolyte engineering is emerging as a key strategy for enhancing the cycle life of lithium metal batteries (LMBs). Fluorinated electrolytes have dramatically extended cycle life; however, intractable challenges regarding the...The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry

DOI: 10.1039/D4EE03862B, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Electrolyte engineering is emerging as a key strategy for enhancing the cycle life of lithium metal batteries (LMBs). Fluorinated electrolytes have dramatically extended cycle life; however, intractable challenges regarding the...
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry