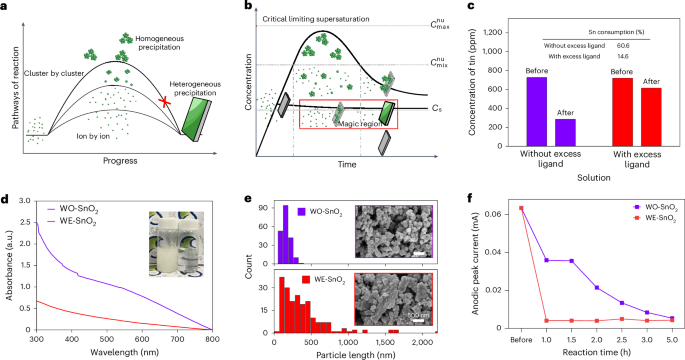
Harnessing Nanohybridized Niclosamide for Precision Mpox Therapeutics
Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 14, Issue 14, May 28, 2025.

This study investigates the potential of nanohybridized niclosamide as a therapeutic agent for Mpox, focusing on enhanced bioavailability, improved antiviral efficacy, and controlled drug release achieved through nanoengineering. The research emphasizes significant advancements in formulation strategies, mechanistic insights, and therapeutic outcomes, underscoring its relevance in precision medicine. The findings position nanohybridized niclosamide as a promising antiviral treatment, addressing existing challenges in Mpox therapy and paving the way for future clinical applications.
Abstract
Niclosamide, initially developed as an anthelmintic, has recently emerged as a potential antiviral, showing efficacy against diverse viral threats, including Mpox. As the global health landscape faces recurrent Mpox outbreaks, repurposing niclosamide through advanced material strategies offers promising therapeutic avenues. This article explores the antiviral mechanisms of niclosamide, focusing on how innovative nano-hybrid formulations enhance its bioavailability and pharmacological performance. By leveraging nanohybridization, niclosamide's limitations—such as poor solubility and bioavailability—are addressed, enabling targeted delivery and sustained release. Early preclinical studies reveal that niclosamide disrupts Mpox replication and entry processes, suggesting its utility as a therapeutic option against poxvirus infections. Looking forward, further in vitro, animal models, and clinical investigations are essential to optimize its application and dosing for Mpox. With continued development in advanced materials, nanohybrid niclosamide could become a critical tool in managing Mpox and related viral threats, offering an accessible, cost-effective option for outbreak preparedness.




























![New York City Officially Has Mechanical Garbage Trucks Now [Update]](https://www.jalopnik.com/img/gallery/new-york-city-officially-has-mechanical-garbage-trucks-now/l-intro-1749064637.jpg?#)