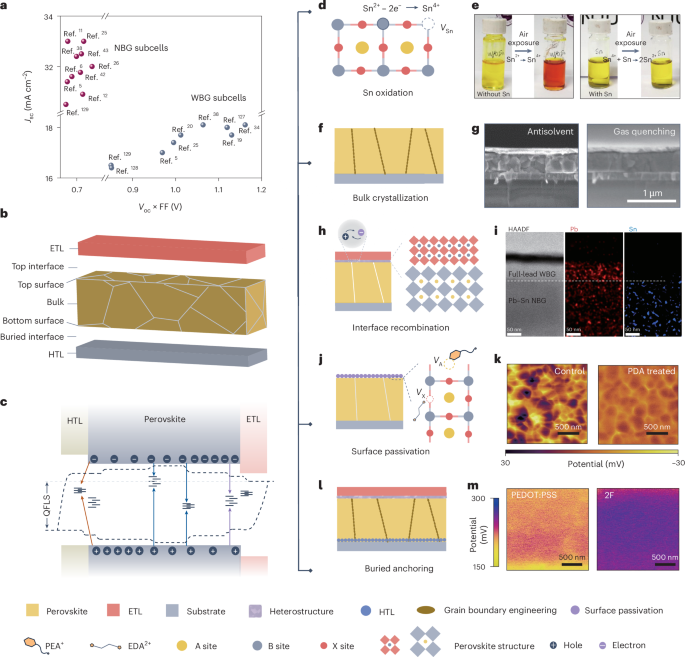
Trump Administration Tariff Updates – June 19, 2025
With the July 9 deadline for finalizing trade deals approaching, the Trump administration is advancing its global tariff strategy. This report outlines the latest developments in tariff implementations and ongoing negotiations with key trading partners. Details of U.S.-China Trade Deal High-level negotiations in London, concluded on June 10, 2025, have produced a framework agreement with […] The post Trump Administration Tariff Updates – June 19, 2025 appeared first on FreightWaves.

With the July 9 deadline for finalizing trade deals approaching, the Trump administration is advancing its global tariff strategy. This report outlines the latest developments in tariff implementations and ongoing negotiations with key trading partners.
Details of U.S.-China Trade Deal
High-level negotiations in London, concluded on June 10, 2025, have produced a framework agreement with China, pending final approval from Presidents Trump and Xi. The deal stabilizes trade relations, with minor issues remaining, particularly around China’s rare earth export controls. The U.S. seeks guaranteed semiconductor supply access to counter China’s leverage. The agreement builds on the May 2025 Geneva consensus and includes the following tariff structure on Chinese imports:
- A baseline reciprocal tariff of 10%, applied to all Chinese goods under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA), effective April 5, 2025.
- An additional 20% tariff on specific Chinese imports, tied to China’s efforts to curb fentanyl precursor shipments to the United States, implemented in February 2025.
- A 25% tariff on certain goods under existing Section 301 provisions, targeting unfair trade practices such as intellectual property theft.
Tariff Composition Clarification: The tariffs are not a flat 10% rate. All Chinese imports face the 10% baseline tariff; specific goods linked to fentanyl precursors incur an additional 20% (totaling 30%); and certain goods under Section 301 face the 25% tariff, which stacks with the 10% baseline (totaling 35%). For example, electronics under Section 301 face 35%, while non-fentanyl, non-Section 301 goods (e.g., apparel) face only 10%. This structure addresses trade imbalances, fentanyl flows, and past trade abuses while incentivizing compliance.
Global Trade Negotiations
As the July 9 deadline nears, the administration has categorized trading partners into two groups:
- Good Faith Negotiators: Countries actively pursuing trade agreements, such as Canada and Japan, are likely to receive deadline extensions.
- Non-Cooperative Nations: Countries deemed uncooperative, such as India, face punitive high tariffs, potentially up to 50%.
The G7 summit in Canada earlier this week served as a platform for bilateral trade discussions. President Trump held meetings with several nations, including the European Union. However, initial EU negotiations stalled over reciprocal trade terms, and subsequent meetings were canceled when the president departed the summit early, threatening a 50% tariff on EU imports if no deal is reached by July 9. China and the EU are preparing retaliatory tariffs, with China eyeing 25% tariffs on U.S. soybeans and the EU planning 25% tariffs on U.S. whiskey and soybeans if the 50% tariff materializes. For now, the only country that has signed a trade deal since Liberation Day is the U.K.
Economic, Legal, and Political Impacts
Economic Impacts: The Federal Reserve announced on June 18, 2025, that it will maintain current interest rates, reflecting several economic factors:
- A surge in U.S. imports, contributing to a $200 billion Q2 trade deficit, is straining economic growth.
- The administration’s tariff policies, generating $10 billion in customs revenue from the 10% baseline tariff, are projected to increase consumer prices by 3-5% and drive inflation.
- The Federal Reserve faces challenges in forecasting the tariff plan’s broader economic impact, with potential GDP reductions of 0.5-1% by 2026.
Legal and Political Developments:
- Lawsuit Updates: Learning Resources, a family-owned toy company, alongside retail coalitions, has petitioned the Supreme Court directly, seeking to bypass the Appeals Court to challenge whether the President exceeded his authority in implementing the global tariff plan. The Learning Resources v. Trump case continues to draw attention, with the Appeals Court’s May 29, 2025, stay allowing tariffs to remain in effect. The Department of Justice is preparing a robust defense, arguing that IEEPA grants broad presidential authority. Growing business coalitions, including toy and retail associations, may join the suit, potentially increasing pressure on the Supreme Court to consider an expedited review despite its term ending soon.
- Congressional Pushback: Bipartisan senators introduced a bill on June 17, 2025, to limit presidential tariff authority under IEEPA, citing economic disruption. While unlikely to pass before July 9, it signals rising political friction, with moderate Republicans joining Democrats in criticizing the tariff plan’s scope.
Emerging Trends:
- Supply Chain Shifts: Companies are accelerating nearshoring to Mexico to mitigate tariff costs. The Mexican Government reported a 165% surge of new foreign direct investment into the country in Q1 2025, driven by tariff fears, with sectors like automotive and electronics leading the trend.
- Global Retaliation Risks: China, the EU, and Canada are preparing retaliatory tariffs targeting U.S. agriculture and energy exports. A June 19, 2025, Reuters report cites EU plans for 25% tariffs on U.S. whiskey and soybeans if the 50% tariff threat materializes, which could escalate trade conflicts post-July 9.
The post Trump Administration Tariff Updates – June 19, 2025 appeared first on FreightWaves.