Si Microanemones Integrated Microfluidic Chip for Highly Efficient Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles
Advanced Healthcare Materials, EarlyView.

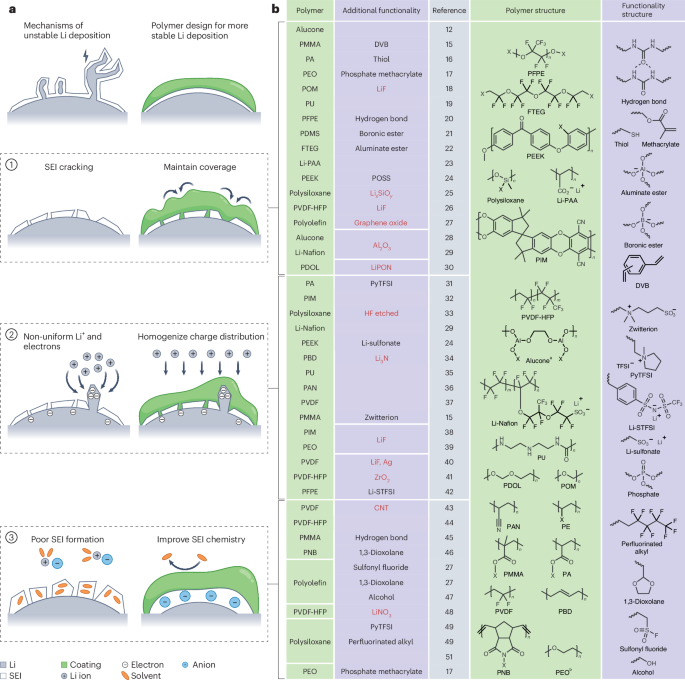
A 3D bio-inspired silicon microanemone chip is designed for efficient extracellular vesicle (EV) isolation from cancer cells, achieving an 89.4% efficiency. The integrated pyramid and nanorod structure increases surface area and binding sites, while intensifying fluid mixing and EV-antibody binding. The cost-effective and reusable chip demonstrates promising potential in advancing cancer detection.
Abstract
Liquid biopsy has emerged as a transformative approach for early cancer detection and treatment monitoring, offering significant potential to improve patient outcomes. However, isolating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) from body fluids is often impeded by background noise, making subsequent analysis challenging. Herein, a bio-inspired 3D silicon microanemone (SMA) microfluidic chip is reported. This innovative structure is prepared by a two-step lithographic method combined with nanosphere lithography, achieving an impressive isolation efficiency of 89.4%. Simulation results reveal that the hierarchical structure not only provides more antibody binding sites but also synergizes with an integrated chaotic mixer to amplify fluid perturbations, while inducing a flow around circular cylinder phenomenon to enhance EV-antibody interactions. Finally, the SMA chip's performance is assessed with clinical samples and combined with RT-qPCR-based β-actin (ACTB) mRNA quantification in purified EVs. The results demonstrate its high sensitivity and specificity in isolating cancer-related EV subgroups, enabling non-invasive and precise detection of cancer biomarkers in blood samples.




















































































![The F-35’s future: The power and cooling competition that could change everything [Video]](https://breakingdefense.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2024/09/240924_F35_moon_USAF-scaled-e1727200160419.jpg?#)