Synergistic Provoking of Pyroptosis and STING Pathway by Multifunctional Manganese‐Polydopamine Nano‐Immunomodulator for Enhanced Renal Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
Advanced Healthcare Materials, EarlyView.

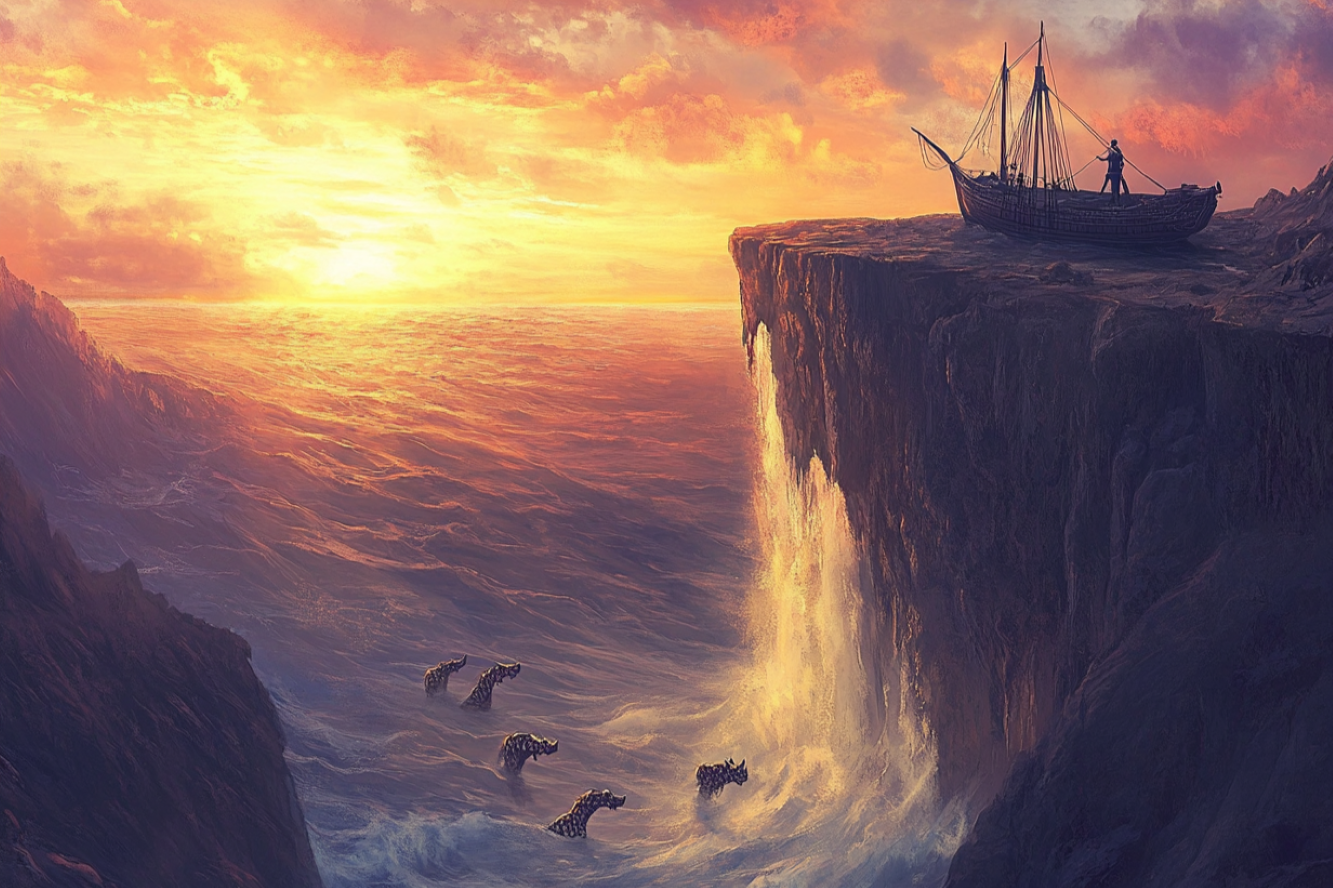
The synthesis process of PDA-Mn-HA NPs and a schematic illustration of its application as a multifunctional nano-immunomodulator in renal cell carcinoma. PDA-Mn-HA NPs exert durable tumoricidal efficacy by inducing tumor pyroptosis through ROS-caspase-3-GSDME signaling pathway, and synergistically inducing the pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines expression of macrophages through ROS-STING-p38/MAPK pathway.
Abstract
Manganese ions are known to enhance anti-tumor immunity by activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. However, precise modulation of the tumor microenvironment using manganese ions remains a challenge. Dopamine, with its controlled release properties within the tumor microenvironment, offers significant potential for precision drug delivery systems. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC), being refractory to conventional treatments, necessitates innovative therapeutic approaches. In this study, a multifunctional manganese-polydopamine nano-immunomodulator coated with hyaluronic acid (PDA-Mn-HA NPs) is developed. These nanoparticles selectively bind to CD44 molecules, which are highly expressed in tumor-associated macrophages and RCC cells, and release manganese ions in a tumor microenvironment-responsive manner. Treatment with PDA-Mn-HA NPs effectively induces macrophage M1 polarization, triggers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Transcriptomic analysis reveals that PDA-Mn-HA NPs polarize and activate macrophages through the reactive oxygen species(ROS)-STING-p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Additionally, PDA-Mn-HA NPs induce ROS-caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis in RCC cells via a Fenton-like reaction. In RCC mouse models, PDA-Mn-HA NPs remodel the macrophage-mediated immune microenvironment, enhance immune cell infiltration, and significantly suppress tumor growth. In conclusion, multifunctional PDA-Mn-HA NPs demonstrate translational potential by addressing the limitations of precision manganese delivery and achieving synergistic targeting of macrophages and tumor cells, offering a promising therapeutic strategy for RCC.