Orally Deliverable Iron‐Ceria Nanotablets for Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 14, Issue 8, March 25, 2025.

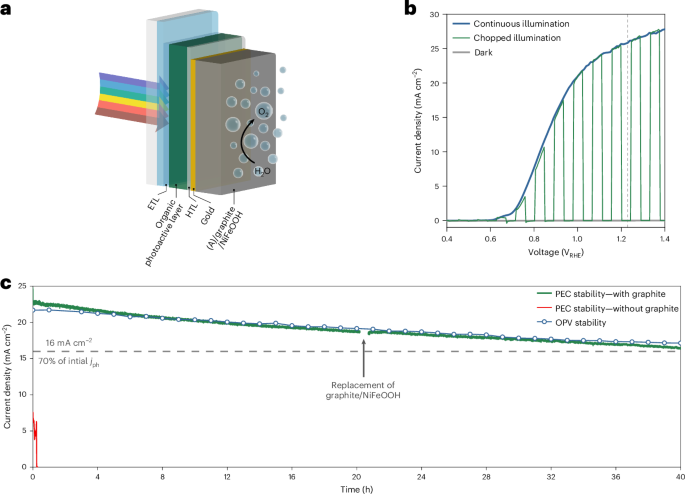
For enteric delivery of ceria-based anti-inflammatory nanozymes, iron-ceria nanoparticles with lower toxicity and higher catalytic activity are formulated into iron-ceria nanotablets (CFNT). Orally administered CFNT provides therapeutic efficacy on the enterocolitis model in vivo by manipulating the behavior of immune cells, cytokine secretion, and transcription factors toward an anti-inflammatory environment.
Abstract
Ceria-based nanoparticles are versatile in treating various inflammatory diseases, but their feasibility in clinical translation is undermined by safety concerns and a limited delivery system. Meanwhile, the idiopathic nature of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) calls for a wider variety of therapeutics via moderation of the intestinal immune system. In this regard, the synthesis and oral formulation of iron-ceria nanoparticles (CF NPs) with enhanced nanozymic activity and lower toxicity risk than conventional ceria-based nanoparticles are reported. CF NPs are clustered in calcium phosphate (CaP) and coated with a pH-responsive polymer to provide the enteric formulation of iron-ceria nanotablets (CFNT). CFNT exhibits a marked alleviative efficacy in the dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced enterocolitis model in vivo by modulating the pro-inflammatory behavior of innate immune cells including macrophages and neutrophils, promoting anti-inflammatory cytokine profiles, and downregulating key transcription factors of inflammatory pathways.