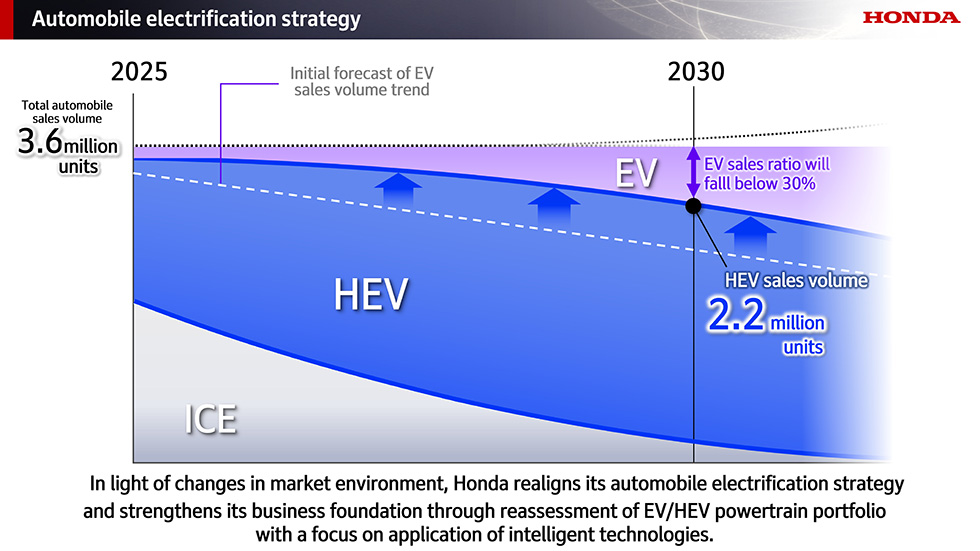
Neutrophil Membrane‐Encapsulated Polymerized Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles Effectively Alleviating Rheumatoid Arthritis by Facilitating Sustained Release of Salicylic Acid into the Articular Cavity from Chondrocytes
Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 14, Issue 12, May 6, 2025.

The TOC graphic is created by Adobe Illustrator CC 2017 Neutrophil membrane-encapsulated polymerized salicylic acid nanoparticles (N-PSAs) which can be precisely targeted to inflammatory regions, consist of a core of polymerized salicylic acid nanoparticles (PSA - NPs) encapsulated by neutrophil membranes. These nanoparticles not only rapidly neutralize inflammatory factors but also penetrate the secondary chondrogenic targets, releasing salicylic acid (SA) within chondrocytes to reduce synovial neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation and inflammation.
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that primarily instigates chronic inflammation in multiple joints. Salicylic acid (SA) is a classic anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of RA. To enhance the therapeutic effect of SA, an innovative therapeutic approach for RA is developed by encapsulating polymerized-SA (PSA) nanoparticles within neutrophil membranes. The study demonstrated that neutrophil membranes endowed PSAs with the ability to selectively target inflammatory joints in RA mice, where they specifically accumulated within the inflammatory chondrocytes. The internalized PSAs underwent gradual degradation into SA within chondrocytes, facilitating sustained release into the articular cavity and effectively alleviating RA symptoms. By attenuating the expression of inflammatory mediators within the joint cavity and suppressing neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in the synovium, neutrophil membrane encapsulated polymerized salicylic acid nanoparticles (N-PSAs) effectively restore long-term intra-articular homeostasis in RA mice, thereby establishing a conducive microenvironment for cartilage repair. In summary, the articular chondrocytes represent an optimal reservoir for therapeutic agents targeting joint disorders. By conferring PSA with the capability to specifically target inflammatory chondrocytes, the neutrophil membrane-coated drug-polymerized nanoparticles offer a promising therapeutic strategy for the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and serve as a valuable reference for treating other inflammatory joint disorders.