This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
All
Autoblog
Autocar RSS Feed
Automotive News Breaking News Feed
Automotive World
Autos
Electric Cars Report
Jalopnik
Automotive News | AM-online
Speedhunters
The Truth About Cars
Isuzu: The announcement of financial informat...
May 14, 2025 0
Pony AI Inc. announces voluntary extended loc...
May 14, 2025 0
Plus completes successful test of semi-autono...
May 14, 2025 0
Iteris chosen to implement the City of Burles...
May 14, 2025 0
All
All Stories
All Stories
BioPharma Dive - Latest News
Breaking World Pharma News
Drugs.com - Clinical Trials
Drugs.com - FDA MedWatch Alerts
Drugs.com - New Drug Approvals
Drugs.com - Pharma Industry News
FDA Press Releases RSS Feed
Federal Register: Food and Drug Administration
News and press releases
Pharmaceuticals news FT.com
PharmaTimes World News
Stat
What's new
Unlocking a new era in liver cancer treatment...
May 12, 2025 0
Fungi dwelling on human skin may provide new ...
May 12, 2025 0
A candidate drug dismantles a metabolic barri...
May 12, 2025 0
FDA Approves Arbli (losartan potassium) Oral ...
May 12, 2025 0
FDA Approves Pembrolizumab for HER2 Positive ...
May 12, 2025 0
All
Breaking DefenseFull RSS Feed – Breaking Defense
DefenceTalk
Defense One - All Content
Military Space News
NATO Latest News
The Aviationist
War is Boring
War on the Rocks
NATO Chiefs of Defence meet in Brussels
May 14, 2025 0
NATO Chiefs of Defence meet in Brussels
May 14, 2025 0
The United Kingdom takes the lead of NATO’s T...
May 13, 2025 0
NATO hosts Colombian Chief of Defence
May 13, 2025 0
Chair of the NATO Military Committee visits t...
May 12, 2025 0
All
Advanced Energy Materials
CleanTechnica
Energy | FT
Energy | The Guardian
EnergyTrend
Nature Energy
NYT > Energy & Environment
PV-Tech
RSC - Energy Environ. Sci. latest articles
Utility Dive - Latest News
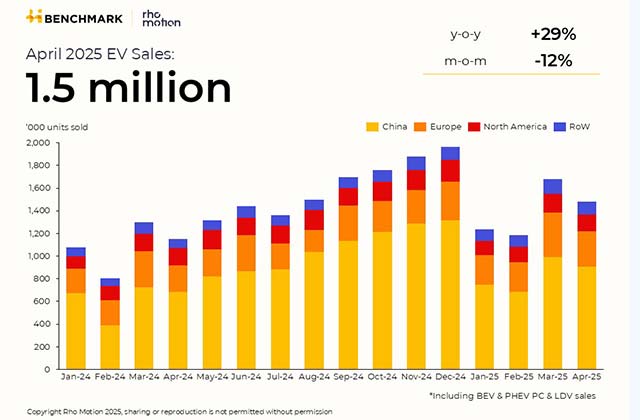
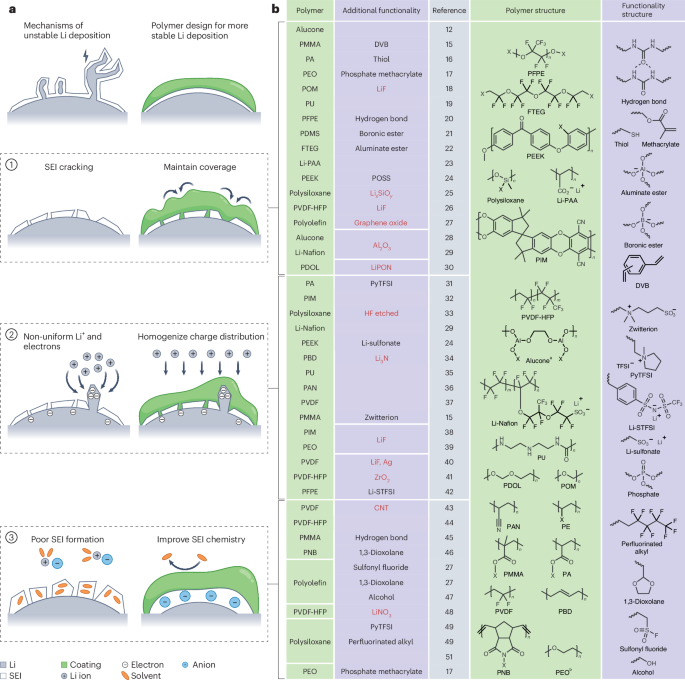
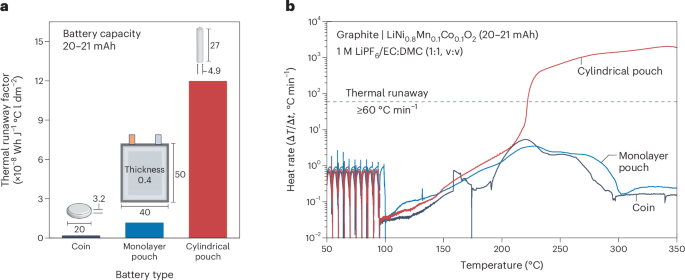
An In Situ Polymerized Solid‐State Electrolyt...
May 14, 2025 0
High‐Performing Perovskite/Ruddlesden‐Popper ...
May 14, 2025 0
Lattice Plainification and Intercalation Adva...
May 14, 2025 0
VS2/Bi2S3 Spring‐Type Heterointerfaces Hollow...
May 14, 2025 0
Understanding non-compliance
May 12, 2025 0
Author Correction: H<sub>2</sub> and CO<sub>2...
May 12, 2025 0
- Contact
- LIVE TV
- Agriculture
- Automotive
- Beauty
-
Biopharma
- All
- All Stories
- All Stories
- BioPharma Dive - Latest News
- Breaking World Pharma News
- Drugs.com - Clinical Trials
- Drugs.com - FDA MedWatch Alerts
- Drugs.com - New Drug Approvals
- Drugs.com - Pharma Industry News
- FDA Press Releases RSS Feed
- Federal Register: Food and Drug Administration
- News and press releases
- Pharmaceuticals news FT.com
- PharmaTimes World News
- Stat
- What's new
- Defense
- Energy & Water
- Fashion
- Food & Beverage
- Healthcare
- Legal
- Manufacturing
- Luxury
- Medical Devices
- Mining
- Real Estate
- Retail
- Science Journals
- Transport & Logistics
- Travel & Hospitality