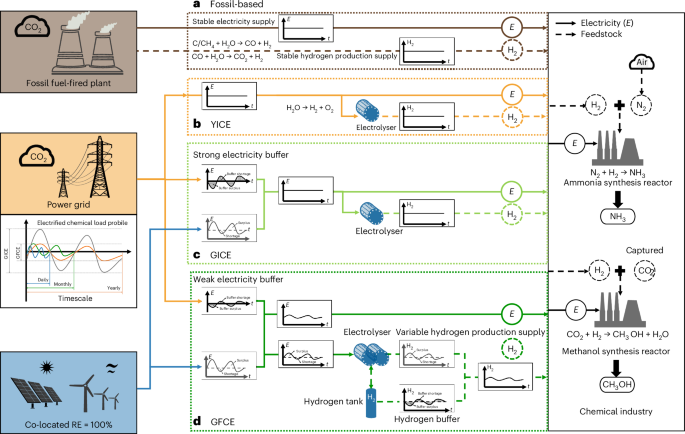
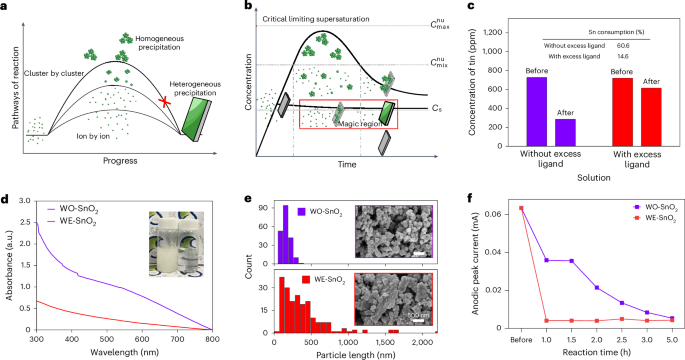
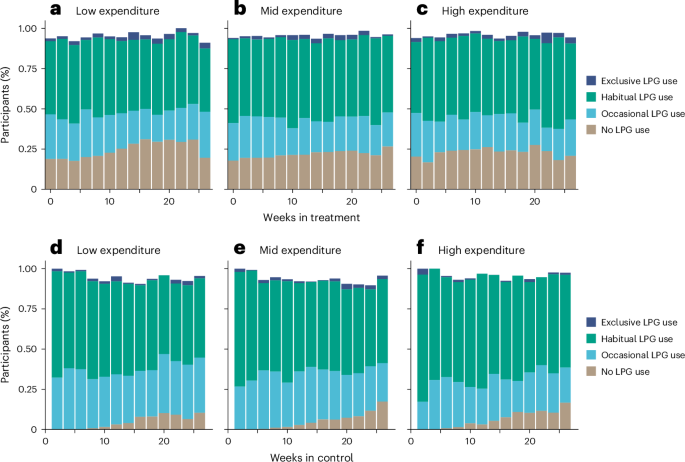
A hormone-dependent tRNA half promotes cell cycle progression via destabilization of p21 mRNA
by Takuya Kawamura, Megumi Shigematsu, Yohei Kirino tRNA halves are among the most abundant short non-coding RNAs in the cellular transcriptome. Here we report that in androgen receptor-positive LNCaP prostate cancer cells, the hormone-dependent 5′-tRNALysCUU half promoted cell proliferation by facilitating cell cycle progression. Global mRNA profiling upon the 5′-tRNALysCUU half depletion revealed that the mRNA of p21, a negative regulator of the cell cycle, is post-transcriptionally destabilized via a 5′-tRNALysCUU half-driven mechanism. YBX1, identified as a protein interacting with 5′-tRNALysCUU half in the cytosol, was shown to stabilize p21 mRNA. Specific sequences resembling the 5′-tRNALysCUU half, located in the 3′-UTR of p21 mRNA and termed LL588, were identified as the binding site for YBX1 and are required for p21 mRNA stability. In vitro binding assays demonstrated that the 5′-tRNALysCUU half is capable of displacing YBX1 from LL588. Collectively, our findings suggest that the 5′-tRNALysCUU half directly binds to and displaces YBX1 from p21 mRNA, leading to the destabilization of p21 mRNA and the promotion of cell cycle progression in hormone-dependent cancers. Our study illuminates the role of tRNA halves in regulating mRNA stability and suggests that this may be part of broader regulatory networks affecting mRNA levels, orchestrated by various tRNA halves and their interacting proteins.
by Takuya Kawamura, Megumi Shigematsu, Yohei Kirino tRNA halves are among the most abundant short non-coding RNAs in the cellular transcriptome. Here we report that in androgen receptor-positive LNCaP prostate cancer cells, the hormone-dependent 5′-tRNALysCUU half promoted cell proliferation by facilitating cell cycle progression. Global mRNA profiling upon the 5′-tRNALysCUU half depletion revealed that the mRNA of p21, a negative regulator of the cell cycle, is post-transcriptionally destabilized via a 5′-tRNALysCUU half-driven mechanism. YBX1, identified as a protein interacting with 5′-tRNALysCUU half in the cytosol, was shown to stabilize p21 mRNA. Specific sequences resembling the 5′-tRNALysCUU half, located in the 3′-UTR of p21 mRNA and termed LL588, were identified as the binding site for YBX1 and are required for p21 mRNA stability. In vitro binding assays demonstrated that the 5′-tRNALysCUU half is capable of displacing YBX1 from LL588. Collectively, our findings suggest that the 5′-tRNALysCUU half directly binds to and displaces YBX1 from p21 mRNA, leading to the destabilization of p21 mRNA and the promotion of cell cycle progression in hormone-dependent cancers. Our study illuminates the role of tRNA halves in regulating mRNA stability and suggests that this may be part of broader regulatory networks affecting mRNA levels, orchestrated by various tRNA halves and their interacting proteins.