STAT+: Tourmaline drug cuts inflammation tied to heart disease
Tourmaline Bio said its experimental antibody treatment demonstrated deep reductions in a measure of inflammation often tied to heart disease

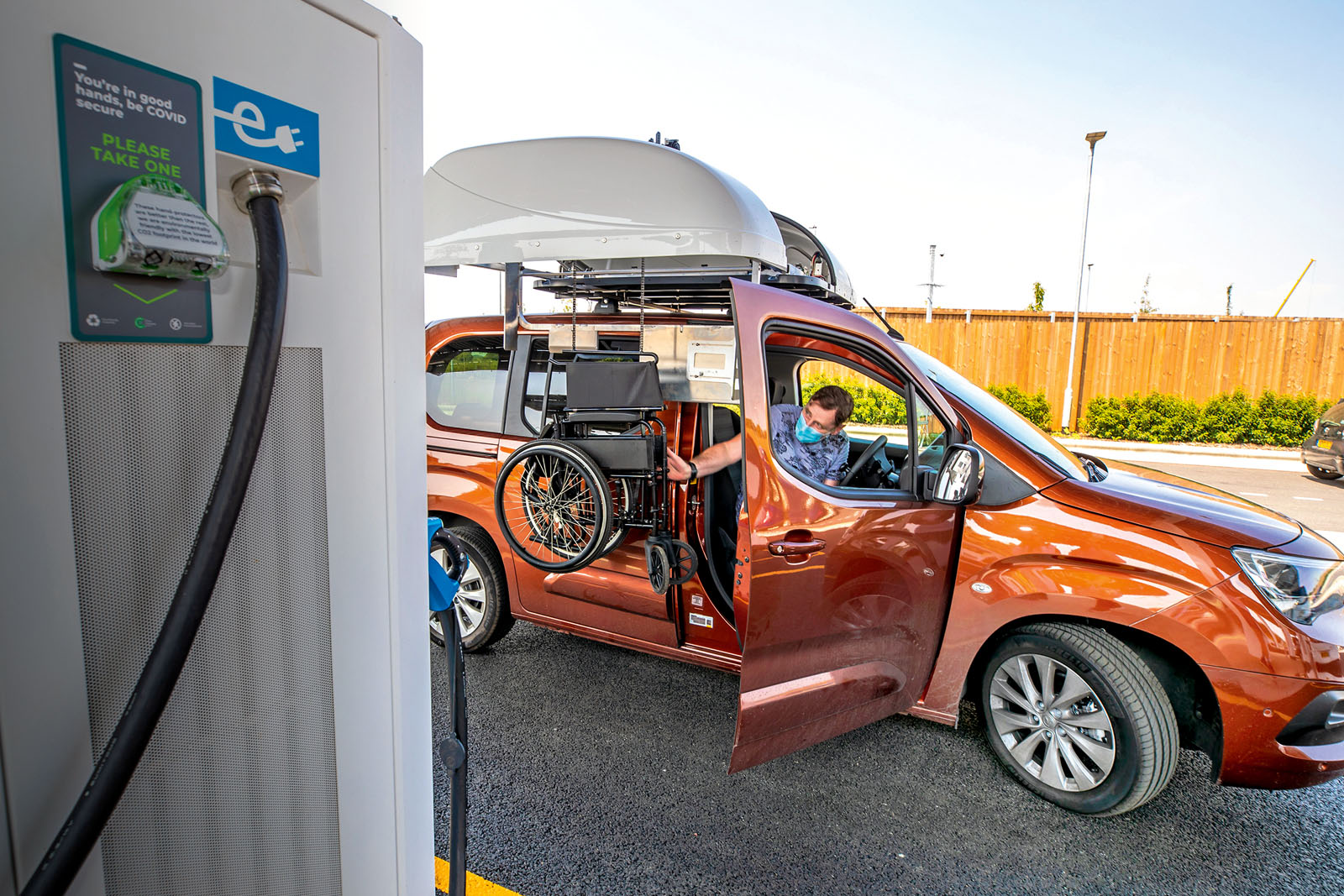
Tourmaline Bio said Tuesday that its experimental antibody treatment demonstrated deep reductions in a measure of inflammation often tied to heart disease, although a high placebo response in the mid-stage study may muddy interpretation of the outcome.
In the Phase 2 study called TRANQUILITY, the highest dose of the Tourmaline drug lowered by 86% the levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), a measure of inflammation, through 90 days. Study participants treated with a placebo showed hs-CRP reductions of 15%.
On an absolute basis, the inflammation-lowering efficacy of the Tourmaline drug, called pacibekitug, was comparable to the results shown previously by Novo Nordisk for its similar heart-disease antibody. But when adjusted for placebo, pacibekitug cut hs-CRP levels by 71% compared to a 84% reduction for the Novo Nordisk drug in its own study.