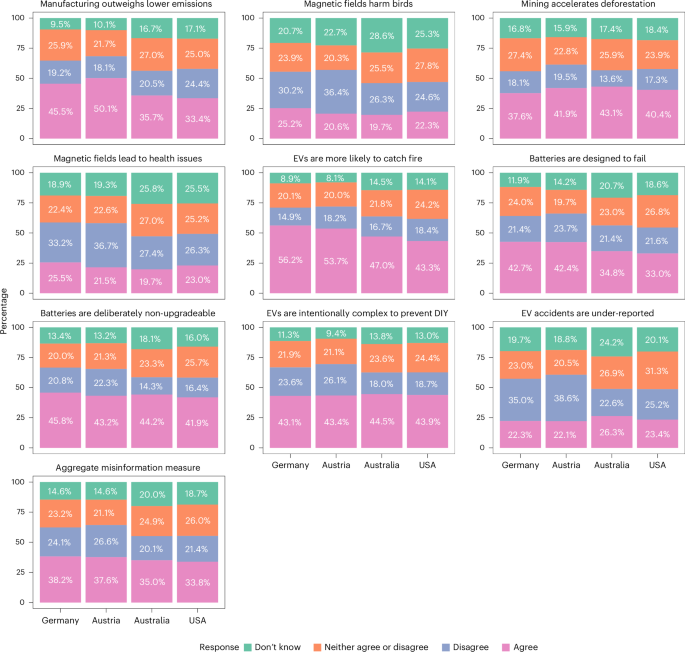
A Smart Hydrogel Dressing Balances Reactive Oxygen Species Levels for Effective Treatment of Bacteria‐Infected Atopic Dermatitis
Advanced Healthcare Materials, EarlyView.

Photosensitizers generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) to exacerbate inflammation, whereas the curcumin/zinc-doped ferricyanide-derived metal-organic framework(Cur/ZnMOF) composite hydrogel scavenges excess ROS and restores oxidative balance through synergistic antioxidant activity. This rationally designed system, combining self-repair, strong adhesion, and mechanical toughness, addresses both pathological mechanisms and clinical needs, thereby providing a novel therapeutic strategy for bacteria-infected atopic dermatitis.
Abstract
Bacteria-infected atopic dermatitis (AD) is an infectious inflammatory skin disease that profoundly disrupts patients' daily lives. As a viable alternative to antibiotic therapy, reactive oxygen species (ROS) treatment has emerged, effectively eradicating bacteria without the risk of antibiotic resistance. Nevertheless, the excess production of ROS can subsequently trigger inflammation in surrounding healthy tissues. To tackle this challenge, a ROS-balancing hydrogel dressing is devised. This dressing integrates a nanocomposite comprising zinc-doped ferricyanide-derived metal–organic framework (ZnMOF) loaded with curcumin (Cur), embedded in a hydrogel matrix of gelatin (Gel) crosslinked with silk fibroin (SF). Upon light activation, the Cur/ZnMOF/SF@Gel hydrogel dressing generates a significant quantity of ROS, enabling rapid bacterial elimination at the infection site. Concurrently, the enzymatic antioxidant activity of ZnMOF and the polyphenolic compounds in Cur within the hydrogel work in synergy to neutralize excess ROS by chelating iron ions, thereby inhibiting the Fenton and Haber–Weiss reactions. This mechanism restores ROS balance and mitigates oxidative stress in the skin tissues. Additionally, the synthesized hydrogel dressing demonstrates remarkable self-healing properties, robust adhesive capabilities, and outstanding mechanical performance. This intelligent, multifunctional hydrogel offers a promising substitute for traditional antibiotic-loaded surgical dressings in the rapid and effective management of bacteria-infected AD.